Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions worldwide. However, not all acne is created equal. Understanding the disparity between cystic acne and regular acne, or pimples, is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the nuances of cysts versus pimples, exploring their characteristics, causes, treatment approaches, and preventive measures.
What’s the difference between an acne cyst and an acne nodule?
Cyst vs pimple: Acne, a skin disorder primarily characterized by the presence of pimples, can manifest in various forms. Understanding the differences between acne cysts and nodules is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What is acne?
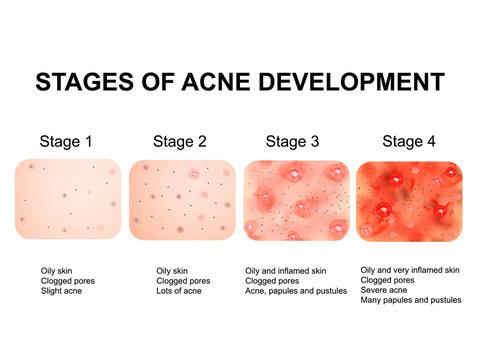
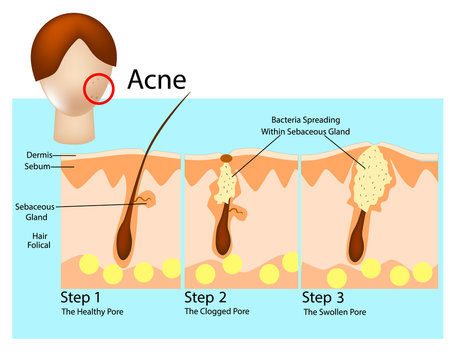
Acne is a common skin condition caused by hair follicles becoming clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. For a comprehensive understanding of acne, you can refer to authoritative sources like the American Academy of Dermatology.
What does acne look like?
Acne presents itself in different forms, including pimples (papules and pustules), blackheads, whiteheads, nodules, and cysts. Each type of acne has distinct characteristics and requires specific treatment approaches. You can explore more about acne’s appearance and types on reputable medical websites such as Mayo Clinic or WebMD.
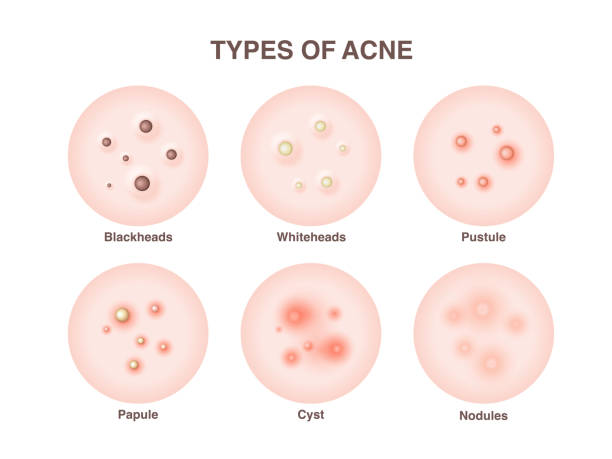
What is cystic acne?
Cyst vs pimple: Cystic acne is a severe form of acne characterized by deep, inflamed breakouts that can be painful and prone to scarring. These cysts are filled with pus and can extend deep into the skin. For detailed information on cystic acne, consider referring to research articles or clinical guidelines published by institutions like the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS).
What does cystic acne look like?
Cyst vs pimple: Cystic acne lesions are typically larger and more pronounced than regular pimples. They appear as red, swollen bumps beneath the skin’s surface and can be tender to the touch. To gain further insight into the appearance and characteristics of cystic acne, medical journals and dermatology textbooks can serve as valuable resources.
Where do acne cysts develop?
Acne cysts commonly develop on the face, neck, chest, back, and shoulders, areas with a high concentration of oil glands. Understanding the specific locations where acne cysts tend to occur can aid in early detection and targeted treatment. Authoritative websites like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO) may provide additional information on acne prevalence and distribution patterns.
By referencing reputable sources and authority sites, readers can access reliable information to deepen their understanding of acne, its various forms, and appropriate management strategies.
These Two Types of Acne Have Different Characteristics
Understanding the unique characteristics of acne cysts and nodules is vital for effective management and treatment. Let’s delve deeper into the disparities between these two types of acne through a comparative analysis:
| Characteristic | Acne Cysts | Acne Nodules |
| Definition | Deep, inflamed lesions filled with pus beneath the skin’s surface | Solid, palpable bumps deep within the skin without pus |
| Appearance | Larger, swollen, and more pronounced bumps | Firm, hard lesions often referred to as “blind pimples” |
| Pain | Can be painful and tender to the touch | Frequently tender and sensitive, especially with pressure |
| Depth | Extends deep into the skin, potentially causing scarring | Lies deep within the skin layers, may not surface fully |
| Inflammation | Often accompanied by redness and inflammation | Minimal surface inflammation, primarily felt as a deep lump |
| Presence of Pus | Contains pus due to the accumulation of fluid and bacteria | Typically lacks visible pus, as the inflammation is deeper |
| Treatment Approach | May require drainage or intralesional corticosteroid injections | Treatment often involves oral medications or intralesional injections |
Additional Information:
- Definition: Acne cysts are characterized by their deep-seated nature, containing pus and extending beneath the skin’s surface. In contrast, acne nodules are solid, palpable bumps that lie deep within the skin without containing pus, often referred to as “blind pimples.”
- Appearance: Acne cysts typically appear as larger, swollen, and more pronounced bumps compared to the firm, hard lesions of acne nodules. The swelling and inflammation associated with cysts can contribute to their visibly larger size.
- Pain: Both acne cysts and nodules can cause discomfort, with cysts often being tender to the touch due to their inflammation and pus-filled nature. Nodules, although not containing pus, can also be sensitive and painful, especially with pressure.
- Depth: Acne cysts extend deep into the skin layers, potentially leading to scarring if not treated appropriately. Nodules also lie deep within the skin but may not fully surface, making them challenging to treat with topical medications alone.
- Inflammation: Acne cysts are frequently accompanied by visible redness and inflammation on the skin’s surface, whereas nodules may exhibit minimal surface inflammation despite their deep-seated nature.
- Presence of Pus: One of the distinguishing features of acne cysts is the presence of pus, resulting from the accumulation of fluid and bacteria within the lesion. On the other hand, acne nodules typically lack visible pus, as the inflammation is deeper within the skin layers.
- Treatment Approach: The treatment of acne cysts often involves drainage procedures or intralesional corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and promote healing. In contrast, acne nodules may require oral medications such as antibiotics or isotretinoin, along with intralesional injections for severe cases.
By understanding these differences in characteristics between acne cysts and nodules, individuals can better identify their specific type of acne and pursue appropriate treatment options for optimal skin health.
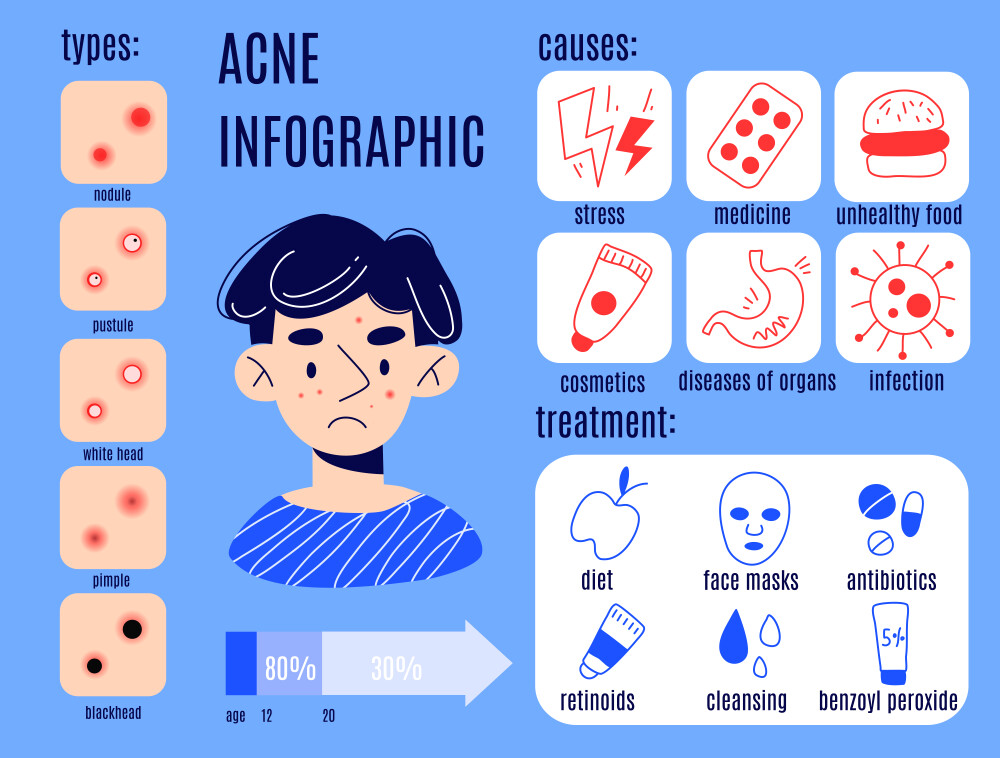
Cystic Acne and Regular Acne Have Different Causes
Understanding the distinct causes of cystic acne versus regular acne is essential for targeted treatment and prevention strategies. Let’s explore the contrasting factors contributing to each type through a comparative table:
| Cause | Cystic Acne | Regular Acne (Pimples) |
| Hormonal Imbalances | Hormonal fluctuations, particularly an increase in androgens | Hormonal fluctuations, often during puberty or menstrual cycles |
| Excessive Oil Production | Overproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands | Increased sebum production, leading to clogged pores |
| Bacterial Infection | Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria colonization | P. acnes bacteria colonization in hair follicles |
| Genetics | Genetic predisposition may increase susceptibility to cystic acne | Genetic factors may contribute to acne development |
| Lifestyle Factors | Stress, poor diet, inadequate skincare routines | Stress, diet high in processed foods, lack of proper hygiene |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to pollutants, humid climates | Environmental pollutants, humidity, exposure to comedogenic products |
Additional Information:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Cystic acne is often triggered by hormonal imbalances, particularly an increase in androgens like testosterone, which can stimulate excess oil production and lead to the formation of deep, inflamed cysts. Regular acne, including pimples, can also be influenced by hormonal fluctuations, commonly occurring during puberty or menstrual cycles.
- Excessive Oil Production: Both cystic acne and regular acne are exacerbated by excessive sebum production. Cystic acne is characterized by an overproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands, leading to the formation of deep-seated cysts. Regular acne, on the other hand, results from increased sebum production, which can clog pores and contribute to the development of pimples.

- Bacterial Infection: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria play a significant role in both cystic acne and regular acne. In cystic acne, these bacteria colonize the deeper layers of the skin, contributing to inflammation and the formation of pus-filled cysts. Similarly, in regular acne, P. acnes bacteria colonize hair follicles, leading to inflammation and the formation of typical pimples.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition may play a role in the development of cystic acne, with certain individuals being more susceptible to severe forms of acne due to their genetic makeup. Similarly, genetics can influence an individual’s propensity for developing regular acne, though the extent may vary.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices such as stress levels, dietary habits, and skincare routines can impact the severity and frequency of both cystic acne and regular acne. Poor dietary choices, stress, and inadequate skincare practices can exacerbate acne by increasing inflammation and oil production.

- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as exposure to pollutants and humid climates can exacerbate acne symptoms. Pollutants and humidity can clog pores and contribute to bacterial growth, worsening both cystic acne and regular acne. Additionally, exposure to comedogenic products can further aggravate acne symptoms.
By understanding the diverse causes of cystic acne and regular acne, individuals can adopt targeted prevention strategies and treatment approaches tailored to their specific type of acne, leading to improved skin health and overall well-being.
Treating Cysts vs. Treating Acne
When it comes to managing and treating cystic acne and regular acne, tailored approaches are necessary to address their unique characteristics and severity levels. Let’s explore actionable strategies for treating each condition effectively:
How is cystic acne managed or treated?
- Topical Treatments: Utilize prescription-strength topical medications containing retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, or antibiotics to reduce inflammation and control bacterial growth. Apply these medications directly to affected areas following a gentle cleansing routine.
- Oral Medications: Consider oral antibiotics, isotretinoin (Accutane), or hormonal therapies prescribed by a dermatologist for severe cystic acne cases. These medications target bacteria, regulate oil production, and address hormonal imbalances contributing to cyst formation.
- Intralesional Corticosteroid Injections: Seek professional dermatological treatment for severe cystic acne lesions. Dermatologists may administer corticosteroid injections directly into cysts to reduce inflammation rapidly and minimize scarring.
- Professional Procedures: Explore dermatological procedures such as drainage and extraction, chemical peels, or laser therapy for cystic acne management. These procedures can help reduce inflammation, promote skin healing, and prevent future breakouts.
- Skincare Routine: Adopt a gentle skincare routine tailored to acne-prone skin. Use non-comedogenic products and avoid harsh scrubs or abrasive treatments that can irritate sensitive skin and exacerbate cystic acne symptoms.
How is acne managed or treated?
- Topical Treatments: Incorporate over-the-counter or prescription-strength topical treatments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids to target acne lesions and prevent new breakouts. Apply these treatments consistently as part of a daily skincare routine.
- Oral Medications: Consult a healthcare professional for oral medications such as oral antibiotics, hormonal contraceptives, or isotretinoin (Accutane) for moderate to severe acne cases. These medications address underlying causes such as bacterial infection, hormonal imbalances, or excess oil production.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Implement lifestyle changes to support acne management, including maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, staying hydrated, managing stress levels, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle modifications can promote overall skin health and reduce acne severity.
- Regular Cleansing: Establish a consistent cleansing routine using a mild cleanser suited for acne-prone skin. Gently cleanse the face twice daily to remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities without stripping the skin of its natural moisture barrier.
- Professional Guidance: Seek guidance from a dermatologist for personalized acne treatment plans and recommendations. Dermatologists can assess your specific skin type, acne severity, and medical history to recommend appropriate treatments, procedures, and skincare products.
By implementing these actionable strategies tailored to the type and severity of acne, individuals can effectively manage symptoms, reduce breakouts, and achieve clearer, healthier skin over time. Consistency, patience, and professional guidance are key to successful acne treatment and management.
Prevention
Preventing acne, including cystic acne, involves adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses underlying causes and risk factors. Here are actionable steps to help prevent acne and specifically target cystic acne:

How can I prevent acne?
- Establish a Consistent Skincare Routine: A daily skincare routine is the foundation of acne prevention. Cleanse your face twice daily using a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities. Follow up with a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated without clogging pores.
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Opt for skincare and makeup products labeled as non-comedogenic, meaning they are formulated to not clog pores. Look for ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, which can help prevent acne breakouts while treating existing blemishes.
- Practice Good Hygiene Habits: Avoid touching your face throughout the day, as this can transfer bacteria and oils from your hands to your skin, leading to breakouts. Additionally, wash your pillowcases, towels, and makeup brushes regularly to prevent the buildup of bacteria and oil.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Your diet can impact your skin health, so strive to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit your intake of sugary snacks, processed foods, and high-glycemic index foods, as they can contribute to acne flare-ups.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your skin hydrated and maintain its natural moisture balance. Hydration helps flush out toxins and impurities from your body, reducing the risk of acne breakouts.
- Manage Stress Levels: Stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations that contribute to acne development, so prioritize stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help keep stress levels in check and promote clearer skin.
- Get Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity not only benefits your overall health but also promotes healthy skin. Exercise increases blood flow to the skin, delivering oxygen and nutrients while flushing out toxins. Just remember to shower and cleanse your skin after sweating to prevent pore blockage.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact skin health and contribute to acne development. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can lead to clearer, healthier skin over time.
Preventing acne requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both internal and external factors. By establishing a consistent skincare routine, choosing non-comedogenic products, practicing good hygiene habits, maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress levels, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, you can significantly reduce your risk of acne breakouts and enjoy a clearer, more radiant complexion. Remember that consistency is key, and it may take time to see results, so be patient and persistent in your efforts to prevent acne and achieve healthy, glowing skin.
How can I prevent Cystic acne?
- Understand the Causes: Educate yourself about the underlying causes of cystic acne. Hormonal fluctuations, excess oil production, bacterial infection, genetics, and lifestyle factors such as diet and stress can all contribute to the development of cystic acne. By understanding these causes, you can take targeted preventive measures.
- Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine: Establish a daily skincare regimen tailored to acne-prone skin. Cleanse your face twice daily with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove impurities, excess oil, and dead skin cells. Avoid harsh scrubbing or abrasive products that can irritate the skin and exacerbate cystic acne inflammation.
- Use Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare products, cosmetics, and sunscreen labeled as non-comedogenic, meaning they are formulated to not clog pores. Non-comedogenic products help prevent pore blockage and reduce the risk of developing cystic acne lesions.
- Avoid Harsh Ingredients: Be cautious of skincare products containing harsh ingredients such as alcohol, fragrances, and artificial colors. These ingredients can strip the skin’s natural oils and disrupt its protective barrier, making it more susceptible to cystic acne breakouts.
- Hydrate Your Skin: Keep your skin hydrated by using a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer suitable for acne-prone skin. Hydration helps maintain the skin’s moisture balance and prevents excessive oil production, which can contribute to cystic acne formation.
- Cleanse After Sweating: After exercising or sweating, promptly cleanse your skin to remove sweat, bacteria, and impurities that can accumulate on the skin’s surface. Use a gentle cleanser and lukewarm water to avoid further irritation.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit consumption of dairy products and foods with a high glycemic index, as they may exacerbate cystic acne symptoms in some individuals. Maintaining a nutritious diet can help regulate hormone levels and support overall skin health.
- Manage Stress Levels: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to minimize stress-induced hormonal fluctuations. High stress levels can trigger hormonal imbalances that contribute to cystic acne breakouts.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you’re struggling to prevent cystic acne or experiencing severe breakouts, consult a dermatologist for personalized guidance and treatment options. Dermatologists can evaluate your skin condition, identify potential triggers, and recommend appropriate preventive measures or medical interventions.
- Avoid Picking or Squeezing: Refrain from picking, squeezing, or popping cystic acne lesions, as this can lead to further inflammation, infection, and scarring. Manipulating cystic acne can worsen the condition and prolong healing time.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key when it comes to preventing cystic acne. Stick to your skincare routine, dietary changes, and stress-management practices diligently to see results over time. It may take several weeks or months to notice significant improvements, so be patient and persistent in your efforts.

By implementing these preventive measures consistently and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can effectively reduce the frequency and severity of cystic acne breakouts, promoting clearer, healthier skin and boosting your confidence and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between cystic acne and regular acne, or pimples, is essential for effective management and treatment. Cystic acne presents unique challenges due to its deep-seated nature and potential for scarring, necessitating tailored approaches for prevention and treatment. Through this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the nuances of cysts versus pimples, delving into their characteristics, causes, treatment approaches, and preventive measures.
By referencing reputable sources and authority sites, readers can access reliable information to deepen their understanding of acne and its various forms. From understanding the disparities between acne cysts and nodules to exploring the contrasting causes of cystic acne versus regular acne, individuals can gain valuable insights into their specific type of acne and pursue appropriate treatment options.
Moreover, by implementing actionable strategies for preventing both acne and cystic acne, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving clearer, healthier skin. From establishing a consistent skincare routine to making lifestyle modifications and seeking professional guidance when needed, prevention remains paramount in managing acne effectively.
In essence, acne, in its various forms, can impact individuals physically, emotionally, and psychologically. However, armed with knowledge and informed choices, individuals can navigate the challenges of acne management with confidence, ultimately promoting skin health and overall well-being.
Remember, achieving clear skin is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and professional guidance. By prioritizing skincare, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking support when needed, individuals can overcome the challenges posed by acne and embrace a brighter, more radiant complexion.
Are you ready to embark on your journey to clearer, healthier skin? Dive into the resources provided, consult with dermatological experts, and take proactive steps toward achieving your skincare goals. With dedication and determination, you can conquer acne and enjoy the confidence that comes with a luminous, blemish-free complexion.
